 The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office today granted Apple a series of 40 new patents, including one that describes various implementations and benefits of a Liquidmetal home button on iPhones and iPads.
The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office today granted Apple a series of 40 new patents, including one that describes various implementations and benefits of a Liquidmetal home button on iPhones and iPads.
Liquidmetal alloys, otherwise known as “bulk solidifying amorphous alloys” in the patent filing (via Patently Apple), have a number of unique properties, including high strength, corrosion resistance, light weight, and malleability.
Apple has annually renewed its exclusive rights to use Liquidmetal since 2010, but how it plans to use the alloys remains unclear. Early speculation centered around Apple using Liquidmetal for the iPhone SIM Tool, while other Liquidmetal home button patents have surfaced as early as 2014. Meanwhile, Steve Zadesky, named on this and other Liquidmetal patents, recently announced he was leaving Apple.
Today’s patent explains how Liquidmetal’s high elasticity makes it an ideal material for a pressure-sensitive home button that would deform slightly when pressed, but return to its normal shape when you remove your finger or thumb. Liquidmetal would always retain this elasticity, while other materials like titanium or stainless steel could become irreversibly deformed and adversely affect the home button.
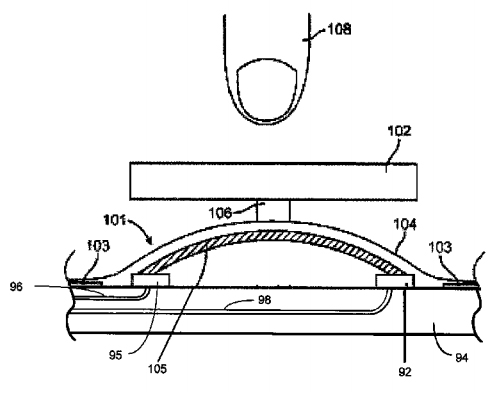
A second embodiment of the patent details a home button with a switch comprising a small actuator positioned adjacent to Liquidmetal material, whereby pressing the actuator deforms the bulk solidifying amorphous alloy. The efficient design could be easier for Apple to manufacture compared to conventional pressure-sensitive home buttons that use dome switches placed on a substrate with or without an actuation nub.
It does not appear that Apple’s upcoming products, including the rumored iPhone SE, iPhone 7, and new 9.7-inch iPad Pro, will adopt Liquidmetal, given the absence of any recent rumors surrounding the alloys, but Apple’s continuous renewal of the material implies it remains interested. It is common for Apple to patent inventions that are not publicly released until years later, if ever.
United States Patent No. 9,279,733 describes Apple’s invention in more detail.
Discuss this article in our forums
Source: MAC ROUMORS
